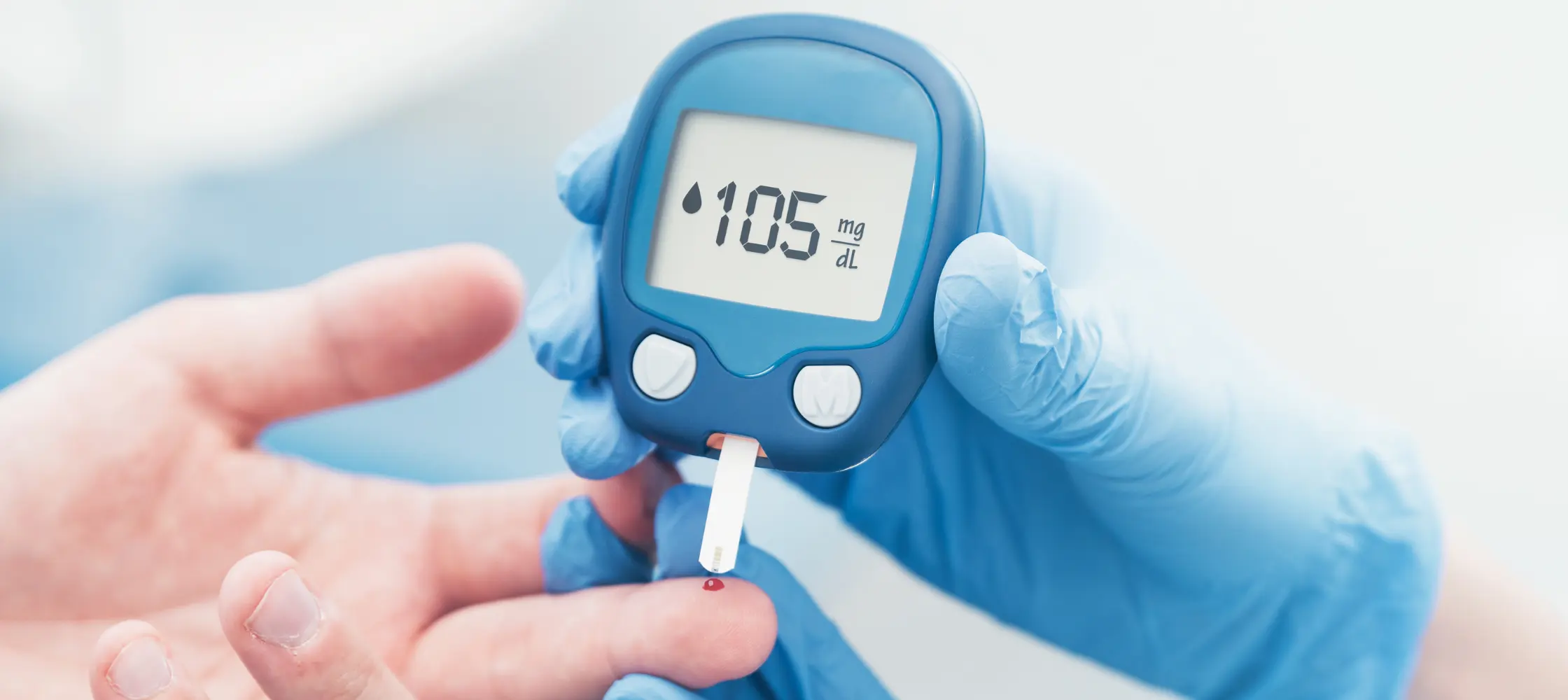
Diabetes is a lifestyle disease that has made India the 'Diabetes capital of the world.'
The Indian Council of Medical Research did a recent study that indicates that the nation has 101 million individuals affected by diabetes. Furthermore, the study shows how an additional 136 million individuals are classified as pre-diabetic, emphasizing the urgent need for preventive measures.
Well, in all this, it is essential to know what diabetes is.
The food we eat gets broken into sugar. It is this sugar that the cells need to give us energy. But for someone suffering from diabetes or pre-diabetes, the sugar-handling system of the human body goes for a toss.
The body struggles to regulate the sugar (glucose) levels in the bloodstream. It can happen due to insufficient insulin production or the body's cells becoming resistant to insulin's effects.
So, diabetes is like a hiccup in your body's sugar processing, making it a bit harder for your cells to get the energy they need.
Diabetes is of two types:
Diabetes and pre-diabetes affect how your body regulates blood sugar (glucose). The symptoms of diabetes and pre-diabetes can vary, and some people may not experience any noticeable symptoms. It's important to note that these conditions can often be asymptomatic, especially in the early stages. Here are some common symptoms associated with diabetes and pre-diabetes:
Common Symptoms of Diabetes:
Symptoms of Pre-Diabetes:
It doesn't cause noticeable symptoms, but some people might experience the same symptoms as diabetes.
These symptoms may go unnoticed but try to keep a watch on them if they disrupt your daily routine and lifestyle.
Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes are manageable and controllable to some extent with advancements in medical science, but they require different approaches as the factors causing them differ.
Here's a brief on how you can control each type of diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes: The primary reason for Type 1 Diabetes is a genetic predisposition. People with type 1 diabetes do require lifelong insulin therapy. It becomes a mandatory way to manage their blood sugar levels.
Here's how to control type 1 diabetes:
Insulin Therapy: Regular insulin injections or pumps are necessary to replace the missing insulin. The dosages are made in consultation with the doctor after they assess each individual's needs.
Blood Sugar Monitoring: You must regularly check your blood sugar levels using a glucose meter. Checking before meals and at bedtime will help you make necessary adjustments to your insulin doses and daily activities. Though whatever changes you bring, do them after consultation with your doctor.
Healthy Eating: It is time to focus on whole foods, lean proteins, vegetables, and complex carbohydrates. Please note you have to stay away from junk and bad carbohydrates. Counting carbohydrates can help you match your insulin doses with your meals.
Physical Activity: Brisk walking is a regular exercise that may help improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels. Here's what you can do to gain the most out of it:
Brisk Walking
If you plan to start any new exercise which is more strenuous, talk to your doctor beforehand.
Stress Management: Stress levels spike blood sugar levels. Practice stress-relief techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
Type 2 Diabetes: it is mostly considered a lifestyle disease. Thus it requires changes in what you eat, how much you exercise, work-life balance, weight issues, and how well you manage stress. Focus on the following to keep away not only Type 2 diabetes but various other lifestyle diseases.
Both types of diabetes require ongoing medical supervision, guidance, and individual efforts. Unless it is Type 1 diabetes, it is a matter of your lifestyle choices that reflects on your health.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
29 Jan, 2024
29 Jan, 2024
29 Jan, 2024
25 Jan, 2024